ABSTRACT
Background: In the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) reported as 6.1%. The estimated age adjusted incidence is 6/100,000. The more advanced disease stage at presentation reaches up to 40% stage IV. The cure rate with first line of therapy (R-CHOP) reaches up to 70%. The CD 19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy targets CD19-expressing B cells and shows efficacy against B-cell lymphomas.
Objective: The registration of CAR-T therapy products at KSA was in 2020 for Tisa-Cel and 2022 for Axi-Cel. The objective is to describe the outcome of the more available CAR-T therapy products in relapsed or refractory NHL.
Methods: Retrospective analysis of CAR-T therapy outcome in NHL and compare the outcome of the two products for the same patient's population, using patients' chart electronic file assessment in the tertiary institution treating over 500 new lymphoma per year.
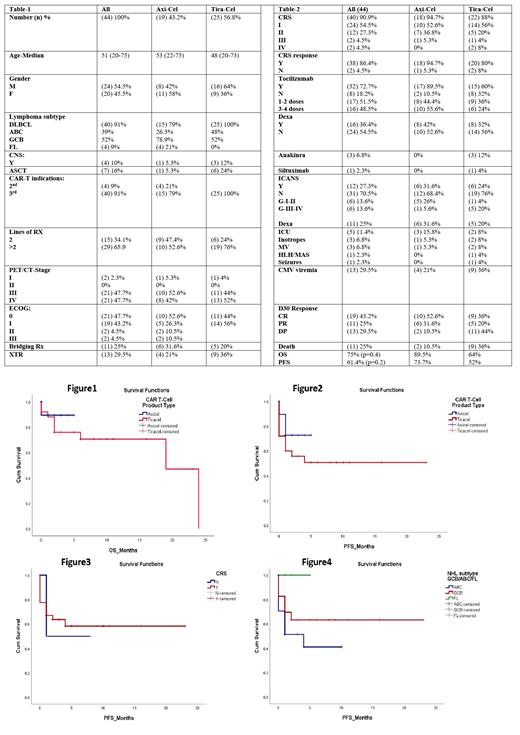
Patients: Between November 2020 and May 2023, 44 patients with relapsed or refractory NHL to ≥2 lines of therapy, Follicular lymphoma (FL) relapsed after three lines of therapy counted for four patients treated with Axi-Cel. All patients received an infusion were included in the analysis. Of the 44 patients, 54.5% were male (n=24), the median age was 51 (20-75), and ECOG was 0-3. NHL subtype includes germinal center B-cell (GCB) 52% (n=23) and activated B-cell (ABC) 38.6% (n=17); the disease stage by PET/CT scan was III (47.7%, n=21) and IV (47.7%, n=21). In Axi-Cel group, 9.1% (n=4) received CAR-T as second line for relapse refractory disease or relapse within 12 months of complete remission (CR) after 1 st line therapy. Other patients received at least two lines of therapy prior to CAR-T infusion; 65.9% received ≥ 3 lines of therapy. Seven patients (16%) relapsed after autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) have received CAR-T therapy Tica-Cel product (n=6). Four patients (9.1%) have controlled CNS involvement at the infusion time. All patients received lymphodepletion (LD) therapy with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide (Flu/Cy). 25% (n=11) needed bridging chemotherapy therapy before LD, radiation therapy (XRT) bridging was counted for 13 patients (29.5%). The patients' characteristics and disease in Table-1.
Results: Overall response rate (ORR), complete responses (CR), partial responses (PR). The respective toxicities include cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurologic events namely ICANS.
The best ORR was 68.2%; 43.2% of the patients had CR and 25% had PR. The disease progression (DP) was 29.5%. In Axi-Cel group, ORR, CR, PR, and DP was 84.2%, 52.6%, 31.6% and 10.5, respectively. In Tica-Cel group; ORR, CR, PR, and DP was 56%, 36%, 20% and 44%, respectively. The estimated 2 years overall survival was 75% in all patients; 89.5% and 64% in Axi-Cel and Tica-Cel, respectively (p=0.47), Figure1. The estimated overall progressive free survival (PFS) was 61.4% with 73.7% in Axi-Cel group and 52% in Tica-Cel group (p=0.2), Figure2, the best PFS was seen in GCB subtype 65.2% vs 47.1% in ABC, (p= 0.05), Figure4. In FL, PFS was 100%, the patient number is small. PFS was 62.5% in-patient with CRS compared with 50% on non-CRS patient, not statistically significant (p= 0.7), Figure3. The main toxicities post CAR-T cell infusion including cytokines release syndrome (CRS) was 90.9% with 9% grade ≥ 3. In Tica-Cel, grade CRS-IV was 9% while 0% in Axi-Cel. Neurotoxicity (NT)-ICANS was 27% with grade ≥ 3 of 13.6% in both groups (20% in Tica-Cel and 5.6% in Axi-Cel). Tocilizumab was used in 72.7% in all cohorts with higher number of patients in Axi-Cel 17/19 (98.5%). Dexamethasone (Dexa) was used in CRS in 36.4%, in Axi-Cel; 42% of patients received Dexa while 32% in Tica-Cel group. In addition, for treatment of ICANS; Dexa was needed in 31.6% of Axi-Cel patients and 20% in Tica-Cel group. Upon the latest patient's follow-up, two patients (10.5%) in Axi-Cel group and 36% (n=9) in Tica-Cel group died from DP. The outcome of both products is summarized in Table-2.
Conclusions: In this single-center retrospective analysis of CAR T-cell therapy in relapsed or refractory NHL or FL in adults, the rates of durable responses were like the real-world data. The best response rate was higher in Axi-Cel group; however, the follow-up duration of disease response is shorter in Axi-Cel group. The toxicity profile is similar in both groups with a bit higher of Grade-III-IV ICANS in Tica-Cel group.
Keywords
NHL, FL, CAR-T, CRS, ICANS
Disclosures
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.